Cylinder Block and Cylinder Liner: Definition, Types, and Functions Explained
What Is a Cylinder Block and Cylinder Liner? Types of Liners Explained
In the world of internal combustion engines, understanding the cylinder block and cylinder liner is crucial for anyone involved in automotive engineering or machine maintenance. These components play a fundamental role in the engine’s performance and longevity. This detailed guide will explain what a cylinder block and cylinder liner are, their functions, and the different types of cylinder liners commonly used in engines.
What Is a Cylinder Block?
A cylinder block, also known as the engine block, is the main structural component of an internal combustion engine. It houses essential parts such as the cylinders, pistons, crankshaft, and other vital components necessary for engine operation. The cylinder block is often made from materials such as cast iron or aluminum to provide strength and durability while ensuring the engine can withstand the stresses produced during combustion.
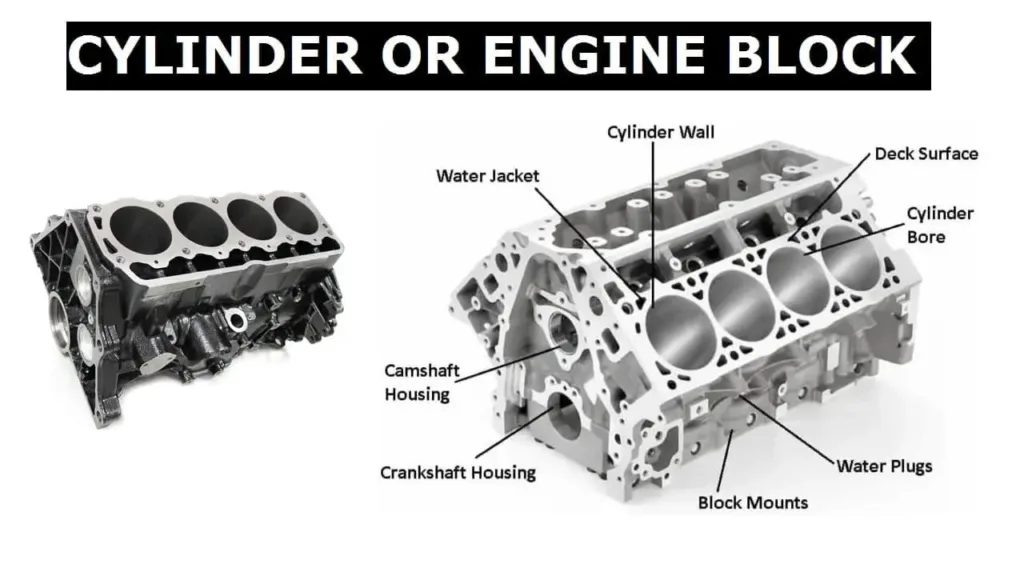
The primary function of the cylinder block is to house the cylinders where fuel combustion occurs. It also provides a pathway for coolant to circulate around the engine to manage temperature, and it supports the bearings and other moving parts within the engine.
What Is a Cylinder Liner?
A cylinder liner is a sleeve or insert placed inside the cylinder of the engine block. The liner acts as a wear-resistant surface where the piston moves up and down. It plays a critical role in protecting the cylinder walls from excessive wear, heat, and pressure generated during engine operation. The cylinder liner ensures smooth piston movement and maintains the integrity of the cylinder.
Cylinder liners are made of materials that can withstand high temperatures and mechanical stresses, such as cast iron or steel. They are designed to be easily replaceable in case of damage or wear, ensuring that the engine remains in optimal condition for as long as possible.
Function of Cylinder Block and Cylinder Liner
The cylinder block and cylinder liner work together to facilitate the proper operation of an engine. Here are the primary functions of both components:
- Cylinder Block: Provides a sturdy and rigid housing for various engine components, including the cylinders and pistons. It also serves to distribute the forces generated during combustion evenly across the engine’s structure.
- Cylinder Liner: Protects the inner walls of the cylinder from wear and tear, heat, and high pressure. It ensures that the piston has a smooth surface to move against and helps in maintaining the engine’s performance over time.
Types of Cylinder Liners
There are several types of cylinder liners used in internal combustion engines, each suited to different engine applications. The choice of liner type depends on factors such as engine design, operating conditions, and maintenance requirements.
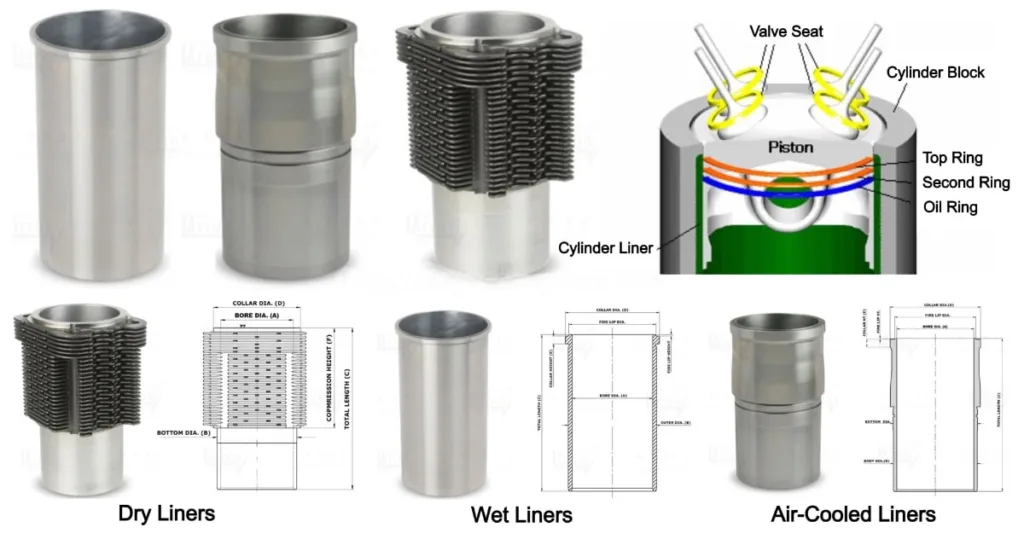
Below are the most common types of cylinder liners:
1. Dry Cylinder Liner
A dry cylinder liner does not have direct contact with the coolant. It fits snugly inside the cylinder block, but there is a gap between the liner and the block. The primary purpose of this design is to isolate the liner from coolant contact, reducing the possibility of corrosion. Dry liners are typically used in smaller engines where the cooling system is separate from the liner, providing easier installation and replacement.
2. Wet Cylinder Liner
A wet cylinder liner is in direct contact with the coolant. This type of liner is typically used in larger engines, such as those found in trucks and industrial machinery, where cooling efficiency is critical. Wet liners help dissipate heat more effectively by circulating coolant around the liner, which prevents overheating and ensures optimal engine performance. These liners are often more challenging to replace compared to dry liners due to the close integration with the engine cooling system.
3. Finish Honed Cylinder Liner
A finish honed cylinder liner undergoes a special process of honing to create a smooth and precise inner surface. This is typically done after the liner is installed, ensuring that the surface is free of imperfections. A honed liner improves the sealing between the piston and the liner, reduces friction, and increases the overall efficiency of the engine. Finish honing is typically used in high-performance engines that require precise engineering for optimal operation.
4. Sleeve-Type Cylinder Liner
A sleeve-type cylinder liner is essentially a removable liner that fits snugly within the engine block, like a sleeve. This design makes it easier to replace the liner when it wears out, making it a popular choice for engines that require frequent maintenance or those that operate under harsh conditions. Sleeve liners are often used in heavy-duty industrial engines, diesel engines, and high-mileage vehicles.
5. Integral Cylinder Liner
An integral cylinder liner is an integral part of the engine block and cannot be removed easily. This type of liner is typically found in engines where the liner is cast directly into the engine block during manufacturing. Integral liners are generally used in smaller engines or those designed for lighter-duty applications. They provide durability and strength but can be more challenging to replace compared to sleeve-type liners.
Materials Used in Cylinder Liners
Cylinder liners are made from materials designed to withstand extreme heat, pressure, and wear. Common materials used include:
- Cast Iron: Cast iron is the most commonly used material for cylinder liners due to its durability, heat resistance, and wear resistance. It provides excellent performance and longevity for most engine types.
- Steel: Steel liners are often used in high-performance engines or applications requiring higher strength and heat resistance. Steel offers superior wear resistance compared to cast iron, making it ideal for heavy-duty engines.
- Aluminum Alloys: Some modern engines use aluminum alloys for liners, particularly in smaller, lighter engines. Aluminum alloys provide good heat dissipation and are lightweight but may not be as durable as cast iron or steel for heavy-duty applications.
Importance of Cylinder Block and Cylinder Liner
The cylinder block and cylinder liner are vital components for engine longevity and performance. Without the protection provided by the cylinder liner, the inner walls of the cylinder would quickly wear out, leading to poor engine performance, excessive oil consumption, and potential engine failure. Proper maintenance and timely replacement of these components can help extend the life of an engine and ensure it continues to operate efficiently.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the cylinder block and cylinder liner, their functions, and the types of liners available is essential for anyone interested in automotive engineering, machine maintenance, or engine repair. The cylinder block serves as the engine’s foundation, while the cylinder liner provides protection and allows for smooth piston movement. The choice of dry, wet, or other liner types depends on the specific needs of the engine and its operating environment. Regular maintenance and the proper selection of materials can ensure that these vital components perform optimally, providing longevity and efficiency to internal combustion engines.
By comprehending the roles of these engine components, individuals can make better decisions when it comes to maintaining, repairing, or upgrading engines to suit their needs.